Inventory of Problems Prone to Occur in the Welding Process of Li Battery Safety Vents
Power batteries provide power for cars, which largely determines the safety, reliability and durability of cars. Laser welding, a special process, is widely used in the manufacturing process of power battery cells and modules.
Take the prismatic cells commonly used in power batteries as an example. Laser welding is utilized for the cover safety vents, poles, and top plate cover and shell. During the process of laser welding of aluminum alloy, it is common to encounter issues such as explosion points, pores, and welding cracks, leading to unqualified results. Hence, it is essential to identify the impact of these unqualified outcomes, analyze their consequences, comprehend the mechanisms of unqualified laser welding. And implement effective measures to enhance the quality and consistency of laser welding during mass production. This approach aims to boost production line output, minimize welding defects, and reduce material wastage.
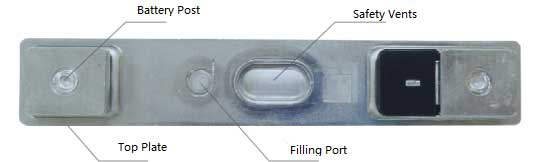
The safety vents of the prismatic cells is a post-welding process. It is a thin-walled valve body on the battery cover. When the internal pressure of the battery exceeds the specified value, the explosion-proof disc valve body will first rupture and release air, releasing pressure to prevent the battery from bursting and causing secondary damage to the car.
The prismatic li battery safety vents are ingeniously designed, often using laser welding to join two aluminum sheets of a specific shape securely. When the internal pressure of the battery reaches a certain level, the aluminum sheet ruptures from a predetermined groove position, halting further expansion and potential explosion.

Common Laser Welding Failures on Li Battery Safety Vents
The main problems that are prone to occur during the welding process of explosion-proof discs include the following aspects and their causes are explained in detail:
Overburning & Perforation
Problem Description
The explosion-proof valve is a thin sheet of pure aluminum with different thicknesses at different locations. When welding with an infrared fiber laser, due to the high reflectivity of solid aluminum to infrared lasers and the thin material, if the welding process is improper, the battery explosion-proof valve is prone to overburning, perforation or explosion during laser welding, causing it to lose its pressure relief and explosion-proof function.
Cause Explanation
- The Laser Power is Too High
During laser welding, if the laser power is set too high, the laser beam will transfer a large amount of energy to the ev battery vents in a very short time, causing its local temperature to rise rapidly to above the melting point, causing the material to melt or even vaporize, forming perforations or explosions.
- Welding Time is Too Long
Welding time is too long will also prevent the battery rupture disc from continuing to be heated, and the heat accumulation exceeds the material’s bearing capacity, causing melting or perforation.
- Material Characteristics
Battery Explosion-proof discs are mostly aluminum sheets, which have high reflectivity to lasers but are also very thin, so they are more susceptible to deformation or melting due to the influence of laser energy.
Welding Quality Problem of Li Battery Safety Vents
Problem Description
The sealing of the weld is crucial to the li battery safety vents. Improper operation or unreasonable welding parameter settings during welding may cause the weld to be unsealed or the weld quality to be unstable.
Cause Explanation
- Improper Control of Heat Input
The control of heat input during welding directly affects the quality of the weld. If the heat input is too large and the temperature in the weld area is too high, it may cause defects such as excessive melting of the weld, cracks or pores; if the heat input is too small, it may cause the weld to be unfused or insufficient in strength.
- Improper Welding Parameter Settings
Welding parameters include welding current, voltage, welding speed, etc. The reasonable setting of these parameters is the key to ensuring weld quality. If the parameter settings are unreasonable, such as excessive current and slow speed, the weld quality may be unstable.
- Material Cleanliness
If the li battery safety vent is not fully cleaned before welding, impurities, such as oil, oxides, etc., on the surface may affect the wettability and bonding strength of the weld, resulting in a decrease in weld quality.
Deformation and Collapse
Problem Description
During the electric welding process, the battery safety vents are prone to melting or deformation, which in turn causes collapse.
Cause Explanation
- Welding Temperature is too High
During the electric welding process, if the welding temperature is too high or the welding time is too long, the battery rupture discs may be partially melted or deformed due to uneven heating.
- Material Thickness and Stiffness
EV battery safety vents are mostly thin sheet materials with relatively small thickness and stiffness. So they are more likely to be deformed by thermal stress during welding.
- Welding Position
The choice of welding position will also affect the deformation of the battery bursting disc. Suppose the welding position is not selected properly, such as welding directly at the center or edge of the li battery safety vents. In that case, the battery rupture disc may be deformed due to uneven heating.
In Conclusion
Throughout the welding process, it is crucial to meticulously control various parameters and process conditions of the lithium ion battery venting to uphold its quality. Simultaneously, the battery safety vents itself must meet specific quality requirements to avoid compromising the welding outcome. A suitable lithium battery safety valves is extremely beneficial for laser welding. It not only demands a tightly sealed weld but also necessitates precise control of heat input to ensure the weld’s breaking pressure value remains stable. Excessive or insufficient heat input can significantly impact the battery’s safety.
